Manufacturing of Tablets by Direct Compression Method
- Share
- publisher
- Steve
- Issue Time
- May 26,2020
Summary
Direct compression method of tablet manufacturing is widely used because it is a time saving process. this method of tablet manufacturing does not contain a lengthy granulation and drying process.
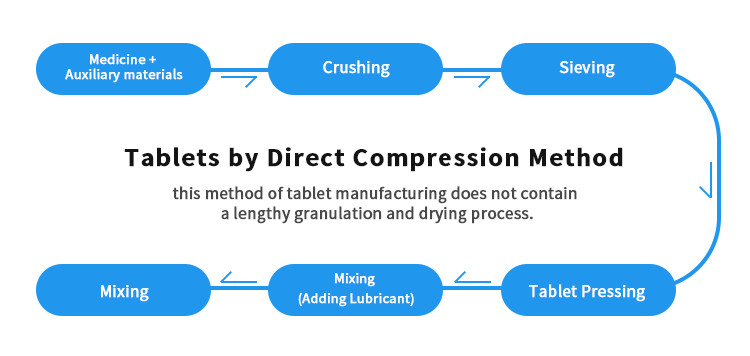
Direct compression method of tablet manufacturing is widely used because it is a time saving process. this method of tablet manufacturing does not contain a lengthy granulation and drying process.
In the past years, the processing of drugs was mostly achieved through wet granulation or related unit operations. Progressively, other methods emerged that revolutionalized and gradually replaced the old tablet manufacturing methods. Amongst the new techniques, the direct compression method uses the most advanced technology.
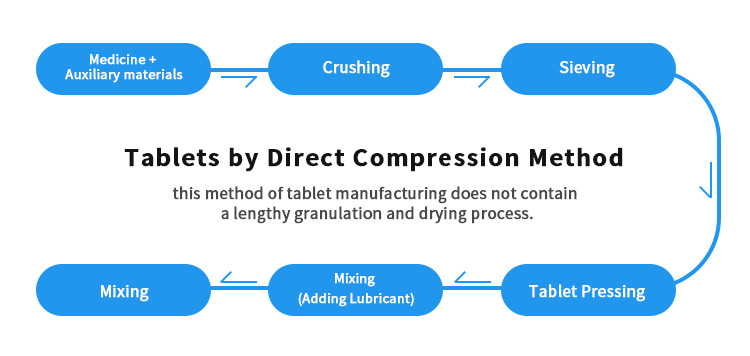
From the term “direct compression“, this method can be defined as basically mixing and processing of formulation ingredients then compressing into tablets. The tablets are obtained directly from the powder API or other excipients. The successful adaptation of this method has lead to a reduction in units of operation, less machinery involvement and minimized processing time.
Manufacturing of tablets using direct compression method involves processes that can be condensed to three. The order following these processes first involves using induced die feeders, dry binders and lastly by using direct compression excipients.
In the process of using induced die feeders, a special feeding device is used. The device prevents segregation and complements the powders to flow down the die cavity of the pharmaceutical tablet compression machine from the hopper. Employing the induce die feeder usually minimizes entrapment of air thereby increasing the density of the filling powder and its susceptibility to compaction. Commonly used for a compact formulation that does not fill the die cavity.
In pharmaceuticals, the use of binders ensures that the active and inactive ingredients are held together. The substances used as dry binders must have the required cohesion properties so as to ensure that the tablets are of the approved hardness and crispiness. It is also recommended that a low binder to drug ratio should be maintained so as to ensure satisfactory sizes of the tablets that contain high doses of drugs. Microcrystalline cellulose and polyethylene glycol are some of the examples of dry binders that are commonly used to manufacture tablets using this technique.

Excipients control the success of the direct compression method. Direct compression excipients can be defined as inert substances that are non-medicinal that are combined as a mixture with drug substances. The overall property of the tablet in regards to component powder fluidity is determined by the direct compression excipient. Other properties that can also be influenced by this include hardness, fragmentation and dissolution. Examples of direct compression excipients that are used for tablet manufacture include fillers, compression aids, disintegrants and lubricants and glidants.
The manufacture of tablets by direct compression is advantageous as the whole process generally requires fewer steps in implementation without requiring the use of moisture and heat. Tablets made as a product of this method have faster dissolution properties as compared to those of wet granulation.
There may be a couple of reasons why direct compression is not suitable for all products. The main reason is that cases of high dosage may present a problem and low dosage may exhibit non-uniform blending.
Direct compression is gradually becoming one of the prevalent and inexpensive tablet manufacturing methods in the pharmaceutical industry. Even though the basic principalities that rule the direct compression method, it is only recently that the method has been fully embraced. The main reason for this is that there has been an introduction of various excipients that are only designed to use with direct compression techniques.